
Can you believe that simply sitting still can pose several health risks?
Even though sitting is a comfortable and relaxing posture, sitting position and duration are closely related to many vital systems of the body, such as the circulatory system, the muscular system, and even the metabolic system. In modern times, people spend more time sitting than sleeping. Therefore, it is important to carefully observe your sitting habits in order to avoid these health problems.
1. Abdominal obesity

Sitting for long periods can cause your waistline to expand. Scientists have studied the relationship between sitting and weight gain. One study explains that when we sit, our bodies move less, so over time the body requires fewer calories per day. However, if our eating habits remain the same, the excess energy is converted and stored as fat.
Sitting is also related to metabolism. Prolonged sitting increases the risk of Metabolic Syndrome, which can lead to obesity. This is because long periods of sitting reduce the activity of lipase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down fat and supporting metabolic processes. If sitting habits are not changed, this risk can persist even if we exercise regularly.
2. Heart disease and the circulatory system

Prolonged sitting also directly affects the heart. When we sit, blood circulation becomes less efficient, reducing the delivery of oxygen and minerals to the body. This increases the risk of fatty acids accumulating and blocking the heart more easily. At the same time, the heart has to work harder to pump blood throughout the body, which may lead to high blood pressure. Research indicates that people who sit still for long periods have up to twice the risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases compared to the general population.
3. Back pain

Back pain is not always caused by lifting heavy objects, sleeping in the wrong position, or exercising incorrectly. Nowadays, back pain often results from sitting for too long, mainly due to daily activities such as watching television or working on a computer.
When we sit, our back bears almost twice as much weight compared to standing. When the back muscles are overworked, fatigue, tension, and injury can occur. This does not even include slouching or sliding down in the chair, which is even more harmful to the back. If prolonged sitting is unavoidable, placing a cushion to support the lower back and keep it upright can help reduce the risk of muscle injury.
4. Stress and emotional health

Sitting does not only affect physical health; it also impacts mental well-being. A study conducted in Australia found that employees who sit continuously for more than six hours a day experience higher levels of stress and anxiety than those who sit for less than three hours a day. The cause may not be the sitting posture or duration directly, but rather the activities performed while sitting, such as working in front of a computer screen all day, which reduces opportunities for face-to-face social interaction.
5. Poor posture
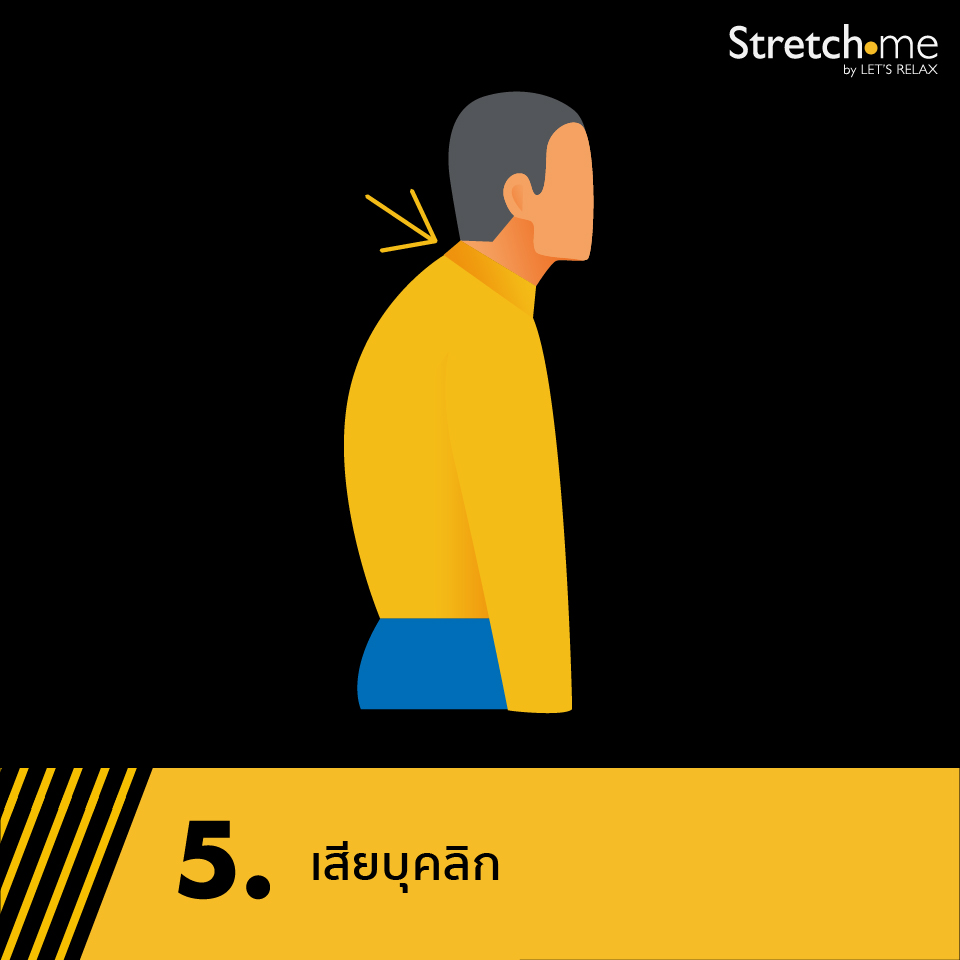
Even without realizing it, the neck, shoulders, and back are the most heavily used parts of the body while sitting, especially during work. A common natural posture is leaning the head forward toward the computer screen, which forces the neck and shoulder muscles to stretch forward as well.
Repeating these postures every day not only causes muscle tightness and injury but also leads to abnormal movement patterns, such as walking with a hunched back, standing with rounded shoulders, or walking with the head thrust forward.